4 Types of Maintenance Strategies – Compared

Reactive Maintenance vs Preventative Maintenance
There is no right or wrong way to look after your mechanical equipment within your building. There is a spectrum though and on one end is Preventative Maintenance (PM) which can be defined as the regular and routine maintenance of equipment and assets in order to keep them running and prevent any costly unplanned downtime from unexpected equipment failure. On the other side of the spectrum is Reactive Maintenance (RM) which refers to repairs that are done when equipment has already broken down. Where do you see yourself falling on this spectrum with your building?

Studies show that PM is the leading maintenance strategy for industries worldwide. Why?? It saves money, mitigates risk, lowers energy consumption, and lengthens the life of the mechanical system. In fact, “you can reduce energy by 30% by proactively looking after your mechanical system” (Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) www.epa.gov). It is also proven that equipment will last longer, therefore, saving money in replacing equipment, “1 dollar in deferred maintenance can equate to $4 in future expenses” (Pacific Partners Consulting Group www.appa.org). Studies also show that in 2020, 76% of companies in the manufacturing industry worldwide prioritized preventive maintenance, this is positive according to Plant Engineering, 2020. Why Nordic looks after our partners this way is because there are huge advantages and benefits to Proactive PM. Let’s review these advantages and disadvantages along with other types of maintenance strategies.
Advantages and Disadvantages
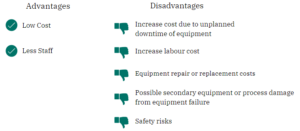
Reactive Maintenance (RM)
As stated previously, RM refers to repairs that are done when equipment has already broken down.
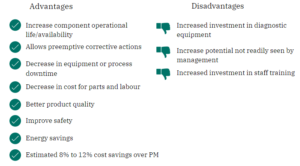
Preventative Maintenance (PM)
As stated previously, PM is the regular and routine maintenance of equipment and assets in order to keep them running and prevent any costly unplanned downtime from unexpected equipment failure.

Predictive Maintenance
“Predictive Maintenance refers to the use of data-driven, proactive maintenance methods that are designed to analyze the condition of equipment and help predict when maintenance should be performed.”
Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)
RCM is defined as a systematic and proactive approach in evaluating, maintaining and ultimately replacing physical assets within a building within its operating context.

In Summary
When compared, RM does have a lower upfront cost than any PM solutions and requires less training to implement. But if you are in it for the long run, PM solutions offer you much more cost savings and energy savings for your business. PM also increases your equipment life expectancy and the safety of your customers and staff. Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) and Predictive Maintenance takes PM to the next level. They’re both efficient strategies that eliminate unnecessary maintenance, emergencies and repairs. “Because RCM is so heavily weighted in the utilization of predictive maintenance technologies, its program advantages and disadvantages mirror those of predictive maintenance. In addition to these advantages, RCM will allow a facility to more closely match resources to need while improving reliability and decreasing cost.” (Sullivan, Pugh, Melendez, & Hunt).
PM helps keep your building running at its best. Stay up to date on your equipment and ensure no surprises down the road. Let’s be proactive and save time and money!
Nordic’s HVAC PM solutions limit unforeseen issues. Our experts can help you implement a customized proactive and preventative maintenance plan for your building today!
Source
Sullivan, G., Pugh, R., Melendez, A., & Hunt, W. (2010). Operations & Maintenance Best Practices, Release 3.0.